gravimetric method of analysis examples|gravimetric factor sample problems : company Gravimetric analysis is a quantitative method for accurately determining the amount of a substance by selective precipitation of the substance from an aqueous solution. . WEBVID_20230628_094609_828 pictures and videos on EroMe. The album about VID_20230628_094609_828 is to be seen for free on EroMe shared by Dedermisterio. .
{plog:ftitle_list}
WEB5,850 Followers, 966 Following, 862 Posts - See Instagram photos and videos from Luana Dias (@luanadiasoficial)
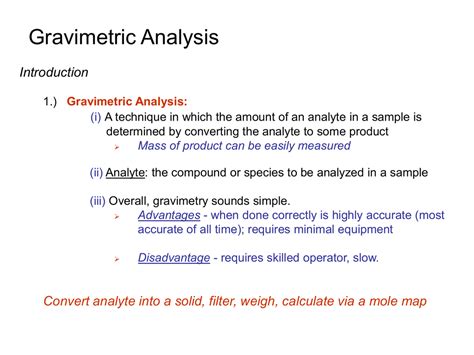
Gravimetric analysis is a method in analytical chemistry to determine the quantity of an analyte based on the mass of a solid. Example: Measuring the solids suspended in the water sample – Once a known volume of water is filtered, . Gravimetric analysis, a method of quantitative chemical analysis in which the constituent sought is converted into a substance (of known composition) that can be separated .
Gravimetric analysis is a quantitative method for accurately determining the amount of a substance by selective precipitation of the substance from an aqueous solution. . Gravimetric analysis is a quantitative method in chemistry that involves determining the amount, or concentration, of a substance present in a sample based on the . An accurate gravimetric analysis requires that the analytical signal—whether it is a mass or a change in mass—is proportional to the amount of analyte in our sample. For all gravimetric methods this proportionality . Gravimetry includes all analytical methods in which the analytical signal is a measurement of mass or a change in mass. When you step on a scale after exercising you .
Gravimetric analysis is a technique through which the amount of an analyte (the ion being analyzed) can be determined through the measurement of mass. Gravimetric analyses depend on comparing the masses of two compounds . Gravimetric analysis is an analytical technique used for the quantitative determination of an analyte based on the mass of solid.The element to be identified is precipitated from a solution using this method of analysis by .Gravimetric analysis describes a set of methods used in analytical chemistry for the quantitative determination of an analyte (the ion being analyzed) based on its mass.
The publication in 1540 of Vannoccio Biringuccio’s Pirotechnia is an early example of applying gravimetry—although not yet known by this name—to the analysis of metals and ores. 1 Although gravimetry no longer is the most important analytical method, it continues to find use in specialized applications.8.1.2 Types of Gravimetric Methods. The four examples in the previous section illustrate different ways in which the measurement of mass may serve as an analytical signal. . An accurate gravimetric analysis requires that the analytical signal—whether it is a mass or a change in mass—be proportional to the amount of analyte in our sample.27. If a precipitate of known stoichiometry does not form, a gravimetric analysis is still feasible if we can establish experimentally the mole ratio between the analyte and the precipitate. Consider, for example, the precipitation .
what is gravimetric analysis simple
In most methods the precipitate is the product of a simple metathesis reaction between the analyte and the precipitant; however, any reaction generating a precipitate can potentially serve as a gravimetric method. Most precipitation gravimetric methods were developed in the nineteenth century, or earlier, often for the analysis of ores. Figure .Gravimetric methods: The . quantitative methods. that are based on determining the . mass. of a . pure compound . to which the . analyte. is . chemically related. • Precipitation gravimetry: The . analyte. is separated from a solution of the sample as a . precipitate. and is converted to a compound of known composition that can be weighed .
Gravimetric analysis is an analytical technique used for the quantitative determination of an analyte based on the mass of a solid. . For example, to determine the sulphate ions (SO 4 2-) . Electro gravimetric method is employed to separate the ions of a substance, often a metal. In this method, the analyte solution is electrolyzed.
In most cases the precipitate is the product of a simple metathesis reaction between the analyte and the precipitant; however, any reaction that generates a precipitate potentially can serve as a gravimetric method. Most precipitation gravimetric methods were developed in the nineteenth century, or earlier, often for the analysis of ores .
An example of a gravimetric analysis is the determination of chloride in a compound. In order to do a gravimetric analysis, a cation must be found that forms an insoluble compound with chloride. This compound must also be pure and easily filtered. The solubility rules indicate that Ag +, Pb 2+, and Hg 2 2+ form insoluble chlorides.
A general principle of gravimetric method of analysis is based on a chemical reaction between analyte and reagent. The analyte (A) of molecules ‘a’ react with the reagent (R) of molecule ‘r’. . Estimation of Fe 2+ by titrating against acidified KMnO 4 is an example of this analysis. The result is obtained in grams. The result is .Gravimetric analysis describes a set of methods used in analytical chemistry for the quantitative determination of an analyte (the ion being analyzed) based on its mass. . several organic functional groups or heteroatoms can be determined using gravimetric precipitation methods • Examples are outlined in Table 8.5 Example 1 • An ore .If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website. If you're behind a web filter, please make sure that the domains *.kastatic.org and *.kasandbox.org are unblocked.
Gravimetric Analysis. A gravimetric analysis is one in which a sample is subjected to some treatment that causes a change in the physical state of the analyte that permits its separation from the other components of the sample. Mass measurements of the sample, the isolated analyte, or some other component of the analysis system, used along with the known stoichiometry of .Example of Gravimetric Analysis: Types of Gravimetric Analysis: Advantages of Gravimetric method: Limitations of Gravimetric method: Difference between Gravimetric and Volumetric analysis: Practice Problems: . the other being the volumetric method. In gravimetric analysis, the amount of an ion present in an analyte is estimated based on the .Gravimetric analysis is a method of a quantitative assessment of laboratory techniques based mostly on the dimension of an analyte's mass. One example of a gravimetric evaluation technique may be used to decide the quantity of an ion in an answer by way of dissolving a regarded quantity of a compound containing the ion in a solvent to break up the ion from its .
Gravimetric analysis and volumetric analysis are two important methods in quantitative chemical analysis. While gravimetric analysis relies on the measurement of mass and the formation of a precipitate, volumetric analysis involves the measurement of volume and the reaction between the analyte and a standardized solution. Types of Gravimetric Methods. The examples in the previous section illustrate four different ways in which a measurement of mass may serve as an analytical signal. . An accurate gravimetric analysis requires that the analytical signal—whether it is a mass or a change in mass—is proportional to the amount of analyte in our sample.%PDF-1.5 %µµµµ 1 0 obj >>> endobj 2 0 obj > endobj 3 0 obj >/XObject >/ProcSet[/PDF/Text/ImageB/ImageC/ImageI] >>/MediaBox[ 0 0 612 792] /Contents 4 0 R/Group .
Example: Calculate the amount of sulphate as barium sulphate from sodium sulphate. Solution of sodium sulphate (Na 2 SO 4) is treated with solution of barium chloride (BaCl 2) to get precipitates of barium sulphate (BaSO 4).The precipitates are then washed, dried and ignited to get free from impurities and then weighed. Na 2 SO 4 + BaCl 2 → BaSO 4 + 2 NaCl Mol. Weight of BaSO 4 .Learn about gravimetric analysis, a method to determine the amount of a substance by measuring its mass. An accurate gravimetric analysis requires that the analytical signal—whether it is a mass or a change in mass—is proportional to the amount of analyte in our sample. . We will return to this concept of applying a conservation of mass later in the chapter when we consider specific examples of gravimetric methods.
GRAVIMETRIC METHOD Gravimetric analysis is a quantitative determination of the amount of analyte through a precipitation process, precipitate isolation, and determination of isolated product weight. . Example: Dimethylglyoxime (DMG) that precipitates only Ni: 2+ Because the release of a volatile species is an essential part of these methods, we classify them collectively as volatilization gravimetric methods of analysis. 8.4: Particulate Gravimetry Precipitation and volatilization gravimetric methods require that the analyte, or some other species in the sample, participates in a chemical reaction.
Learn how to do laboratory investigations in gravimetric analysis. Special emphasis on how to do calculations resulting from data. Specifically we will use g.An accurate gravimetric analysis requires that the analytical signal—whether it is a mass or a change in mass—be proportional to the amount of analyte in our sample. For all gravimetric methods this proportionality involves a . ter when we consider specific examples of gravimetric methods.
Features of Gravimetric Analysis •A given analyte is isolated from the sample and weighed in some pure form. •One of the most accurate and precise methods of macro quantitative analysis. •One of the oldest methods known (before 1810). •Absolute analysis (no standard needed). Weighing sample dissolving (heating-stirring)
steps involved in gravimetric analysis
A simple example of gravimetric analysis is the measurement of solids suspended in a water sample. A known volume of the suspension is filtered and the collected solids are weighed. . Gravimetric analysis, if methods are followed carefully, provides for exceedingly precise analysis. In fact, gravimetric analysis was used to determine the .
Worked Example of Gravimetric Analysis Calculations. The following worked example showed you how to calculate the percent by mass of analyte in a sample using the results of a gravimtric analysis experiment. It demonstrates how to apply the 5 steps outlined in the previous section. . Other methods include volatilisation and electro-analytical .
diesel compression tester amazon
diesel compression tester for tractors
diesel compression tester napa
steps for gravimetric analysis
Um bom aplicativo de aposta esportivadeve ser fácil de usar, especialmente para os jogadores que estão se aventurando nesse mundo pela primeira vez. Quem já . Ver mais
gravimetric method of analysis examples|gravimetric factor sample problems